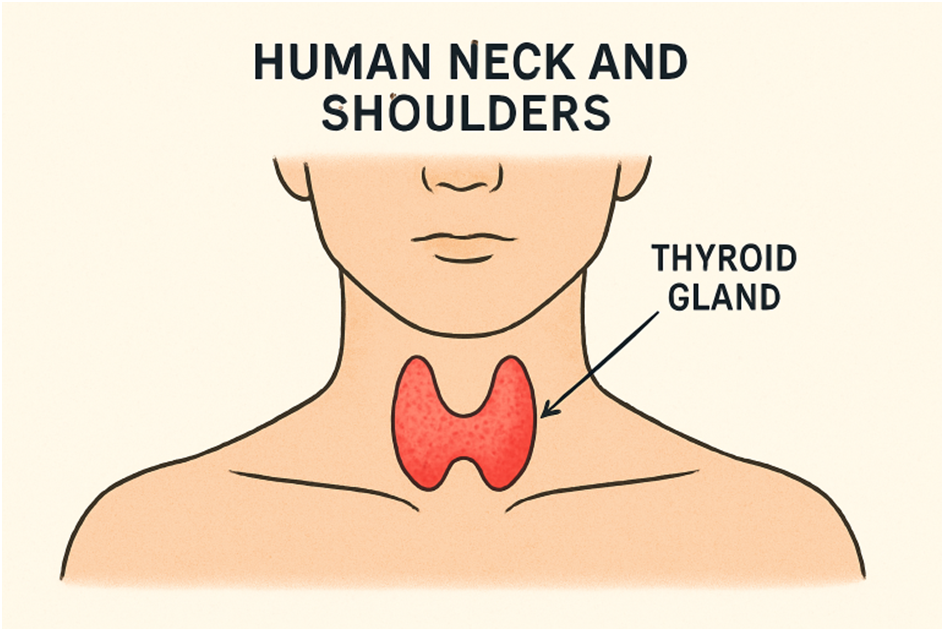
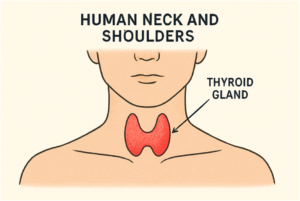
What Is the Thyroid and Why Does It Matter?
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland at the base of the neck, crucial for regulating vital functions. It produces hormones affecting almost every organ, including metabolism, heart rate, temperature, and energy. Dysfunction can cause widespread effects and impact quality of life. Even subtle issues can trigger symptoms such as mood, energy, weight, or changes in skin and hair. Consider thyroid health if you experience unexplained shifts in these areas. Consulting a board certified endocrinologist Miami FL is a key first step to getting an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Thyroid imbalances—hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism—can develop gradually, often mistaken for aging or stress. Recognizing warning signs and understanding their serious implications are crucial for long-term health. With millions affected worldwide, awareness of triggers, family history, and environmental factors helps manage health and prevent complications. Knowing symptoms and when to consult a professional are key to proactive thyroid care.
Common Early Signs to Watch For
Early detection of thyroid disorders can be challenging because the manifestations are often subtle and varied. Still, some core symptoms stand out as red flags:
- Unexplained weight changes – Sudden weight gain might point toward hypothyroidism, while unexpected weight loss is commonly linked to hyperthyroidism. These shifts can occur even when diet and activity levels remain unchanged.
- Fatigue and energy fluctuations – Persistent tiredness or extreme energy highs and lows aren’t always due to a busy lifestyle. Both an underactive and an overactive thyroid can drastically affect your energy levels.
- Changes in hair and skin – Dry, thinning hair, brittle nails, or dry and pale skin may result from thyroid hormone imbalances. Conversely, excessive sweating or soft, velvety skin might suggest an overactive thyroid.
- Memory lapses or mood changes – Depression, anxiety, difficulty focusing, and memory issues can also be linked to thyroid dysregulation, as hormones produced by the thyroid have a strong influence on brain chemistry and emotional health.
Frequent Causes and Risk Factors
Genetics plays a significant role in thyroid health. If you have a family member with thyroid disorders, your risk of developing them increases. Additionally, women(especially those over age 60) are more likely than men to experience thyroid issues, though anyone can be affected.
Environmental and dietary factors also contribute. Iodine deficiency or excess, autoimmune triggers, and exposure to certain medications and toxins can disrupt thyroid function. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides detailed information and statistics on the broad impact of thyroid diseases in the U.S., highlighting the importance of public awareness and early intervention.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice a combination of the symptoms listed above—especially if they’re persistent, worsening, or impacting your daily function—it’s time to consult a healthcare provider. Particular symptoms that need prompt evaluation include rapid or irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, swelling in the neck, and severe mood changes.
Regular physical check-ups become even more important if you have a family history of thyroid disorders. Accurate symptom reporting helps your provider catch subtle problems early, enabling timely and effective interventions.
How Are Thyroid Disorders Diagnosed?
Most thyroid disorders are diagnosed through blood tests and physical exams. Common blood tests measure TSH and thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), while antibody tests may detect autoimmune issues. Physical exams can find goiters or nodules. Imaging techniques, such as ultrasounds or iodine scans, help identify structural or functional problems. These tests are accurate for diagnosis and developing management plans. More info is available at Johns Hopkins Medicine: Thyroid Tests.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Thyroid Health
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, lean proteins, whole grains, and, when appropriate, iodine is essential for supporting thyroid function. Limiting processed foods and excessive soy intake may also benefit certain individuals.
Stress directly affects hormone levels. Incorporating stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise supports overall glandular health. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule and prioritizing rest are also crucial for maintaining hormonal balance.
Current Treatment Options
Treatment for thyroid disorders is highly individual. Most cases of hypothyroidism are treated with synthetic thyroid hormones, while hyperthyroidism may require antithyroid medication, radioactive iodine, or—even in rare cases—surgery. Some structural issues or cancer necessitate surgical solutions as well.
Providers select treatments based on specific patient profiles, balancing effectiveness, safety, and symptom severity. The Endocrine Society offers comprehensive guidance, including questions to ask your doctor and an overview of available treatment options.
Staying Updated: Recent Findings in Thyroid Health
Research in thyroid health is rapidly advancing, with breakthroughs in precision medicine for autoimmune thyroiditis and the development of improved early screening protocols for at-risk populations. Apps and remote tools help patients track symptoms and medication adherence. Staying informed through sources like the Mayo Clinic enables proactive management. Future treatments will be more personalized, less invasive, and supportive, making it easier to maintain thyroid health and overall well-being.